Discover what is hard water, how it affects your home and health, and explore solutions to prevent damage and improve water quality in your household.
What is Hard Water?
You’ve likely heard the term “hard water”
thrown around, but what exactly does it mean, and why should you care? Hard
water is a common issue that affects many households, yet it often goes
unnoticed until its impact becomes more evident. In simple terms, hard water is
water that contains high levels of natural minerals, primarily calcium and
magnesium. While it may not be harmful to your health, hard water can create
significant challenges in your daily life, from damaging appliances to causing
skin irritations. In this article, we’ll break down what is hard water, how to spot it, and, most
importantly, how to deal with it.
What Causes Hard Water?
Hard water gets its name from the high
concentration of minerals, particularly calcium and magnesium, that are
naturally found in certain water sources. As rainwater flows through the
ground, it picks up these minerals from rocks and soil. The more minerals it
picks up, the harder the water becomes.
The difference between hard and soft
water is simple: soft water has a low concentration of minerals, while hard
water has a high concentration. Soft water is generally better for household
tasks like cleaning and washing because it lathers soap more easily and doesn’t
leave mineral deposits behind. On the other hand, hard water can cause a
variety of inconveniences.
What Are the Signs of Hard Water?
Recognizing hard water in your home is
not always straightforward, but there are a few telltale signs to look out for:
●
Scale buildup: This is perhaps the most
obvious sign. You may notice white, chalky deposits on faucets, showerheads,
and in your sinks. This is limescale, a mineral buildup that happens when hard
water evaporates.
●
Cloudy dishes or glassware: If your dishwasher
or hand-washing dishes are often left with streaks, spots, or a cloudy residue,
hard water could be the culprit.
●
Soap scum: Hard water doesn’t mix well with
soap, leaving behind scummy residue on your tubs, showers, and sinks.
●
Skin and hair issues: If your skin feels dry
or itchy after showering, or your hair seems dull and lifeless, hard water
might be to blame.
●
Appliance malfunctions: Hard water can lead to
mineral buildup inside appliances like water heaters, dishwashers, and washing
machines, reducing their efficiency and lifespan.
What Is the Impact of Hard Water on Your
Home?
While hard water may seem like a minor
inconvenience, it can have significant long-term effects on your home and your
wallet:
●
Plumbing problems: Over time, the mineral
buildup in hard water can clog pipes and faucets, restricting water flow and
potentially causing costly plumbing repairs.
●
Damage to appliances: Water heaters,
dishwashers, and washing machines all suffer from mineral deposits. These
deposits can reduce the efficiency of these appliances, leading to higher
energy bills and the need for early replacements.
●
Higher maintenance costs: Whether it’s
replacing appliances or cleaning mineral deposits, the costs associated with
hard water can add up quickly.
What Are the Health Effects of Hard
Water?
When it comes to drinking and bathing,
hard water is generally considered safe. In fact, it can even contribute small
amounts of beneficial minerals to your diet. However, hard water can have some
negative effects on your skin and hair. The mineral content can make skin dry
and more prone to irritation, and it can leave hair feeling dull and brittle.
There are also myths surrounding the
health effects of hard water, such as it causing kidney stones. While drinking
hard water doesn’t directly contribute to kidney stones, the high mineral
content in water can sometimes exacerbate conditions in people who are already
predisposed to such issues.
What Are the Best Solutions for Hard
Water?
If you’re dealing with hard water in your
home, you’re probably wondering what you can do about it. Fortunately, there
are a few different solutions to consider:
●
Water softeners: The most common method for
treating hard water is a water softener, which works by replacing calcium and
magnesium with sodium or potassium ions. There are various types of water
softeners, including salt-based systems, salt-free systems, and
reverse osmosis filters. Choosing the right one depends on your household size,
water hardness level, and specific needs.
●
Reverse osmosis: This is another filtration
method that can remove minerals and impurities from water. It’s highly
effective, but usually used for drinking water rather than the entire home
supply.
●
DIY solutions: For minor issues, you can try
installing a water filter in your shower or using descaling products to remove
buildup in your appliances. However, for long-term solutions, a more
comprehensive water softening system may be necessary.
●
Professional installation: If you’re looking
for a more permanent solution, hiring a professional to install a water
softening system might be the best route. While it’s a larger investment
upfront, it can save you money in the long run by reducing appliance repairs
and maintenance costs.
What is the Cost of Hard Water
Treatment?
The cost of treating hard water depends
on the type of system you choose:
●
Water softeners: A basic water softener can
cost anywhere from $400 to $2,000, depending on the size and features.
Installation costs may be additional, ranging from $100 to $500.
●
Reverse osmosis systems: These typically range
from $150 to $600 for a whole-house system, with installation costs on top.
●
Ongoing maintenance: Water softeners require
regular salt refills (or other maintenance), and reverse osmosis systems need
filter replacements, which can add to the long-term cost.
When deciding on a solution, consider
factors such as the size of your household, the hardness of your water, and how
much you’re willing to invest upfront. While water softeners can be costly
initially, they often pay for themselves by preventing expensive repairs and
appliance replacements.
Hard water may seem like a minor
inconvenience at first, but it can have lasting effects on your plumbing,
appliances, and even your skin and hair. Understanding what hard water is, how
to recognize it, and what solutions are available can help you make informed
decisions about how to protect your home.
If you’ve noticed signs of hard water in
your household—such as scale buildup, cloudy dishes, or skin irritation—it may
be time to consider a water softener or other treatment solutions. Taking
action now can save you time, money, and frustration in the future. Don’t wait
for the damage to accumulate—evaluate your water quality today and explore the
right treatment options for your home.
Alkaline water vs. regular water: Explore the pH differences, health benefits, costs, and risks to help you decide which is best for your hydration needs
Water is essential to life, but when it comes to choosing the best type of water, there's more than just "tap vs. bottled." In recent years, alkaline water has risen in popularity, touted as a health miracle that can do everything from improving hydration to balancing your body’s pH. But is it really all it’s cracked up to be? And how does it compare to regular water, the everyday staple we’ve always relied on? In this article, we’ll explore the key differences, health benefits, and whether alkaline water is really worth the hype.
1. What Is Alkaline Water?
Alkaline water refers to water that has a
higher pH level than regular water. The pH scale, which ranges from 0 to 14,
measures how acidic or alkaline a substance is. Regular water typically has a
neutral pH of 7, while alkaline water has a pH level between 8 and 9.5. But
what makes it alkaline? The answer lies in the minerals that naturally occur or
are added to the water.
Alkaline water is rich in minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium—all
of which contribute to its alkaline properties. Naturally occurring alkaline
water can be found in mineral-rich springs, while artificially alkaline water is created using water ionizers, which
use an electrical process to alter the water's pH.
2. What Is Regular Water?
Regular water, or standard drinking
water, is what most people consume daily, whether it's tap water, bottled
water, or spring water. The pH of regular water is neutral (around 7), meaning
it’s neither acidic nor alkaline. This makes it versatile for all bodily
functions, from regulating body temperature to supporting digestion and
hydration.
The composition of regular water can vary
depending on the source. Tap water typically contains trace minerals like
calcium, sodium, and chloride, which are added by municipal water treatment
processes. Bottled water, on the other hand, might contain slightly different
minerals, depending on the brand and source.
3. The pH Scale: A Key Difference
The pH
scale is a measure of how acidic or alkaline a solution is, ranging from 0
(very acidic) to 14 (very alkaline). Water at a pH of 7 is considered neutral.
Here's where alkaline water stands out:
●
Alkaline water has a pH between 8 and 9.5,
which is slightly higher than neutral.
●
Regular water has a pH of about 7.
In terms of taste, some people find that
alkaline water has a smoother or "softer" flavor due to its higher
mineral content, while regular water can sometimes taste more neutral or even
slightly metallic, depending on the source and mineral composition.
4. Health Benefits of Alkaline Water
One of the main reasons people turn to
alkaline water is for its purported health benefits. Let’s take a look at some
of the most common claims and the science behind them.
●
Hydration: (H2) While there’s no clear
evidence that alkaline water hydrates better than regular water, the added
minerals may aid in better fluid retention in the body. However, your hydration
level largely depends on the volume of water you drink rather than its pH level.
●
Antioxidant Properties: (H3) Alkaline water is
often said to have antioxidant properties, which means it can neutralize
harmful free radicals. Some proponents argue that this can help reduce the risk
of chronic diseases, but the evidence is still limited.
●
Acid-Base Balance: (H3) Some proponents claim
that drinking alkaline water can help balance the body’s pH levels, especially
in people who consume a diet high in acidic foods like meat and processed
foods. However, your body is already equipped with natural mechanisms to maintain
a balanced pH, so the impact of drinking alkaline water may be minimal.
●
Other Claims: (H3) Alkaline water is also
marketed as improving digestion, promoting better skin health, and enhancing
detoxification. While these claims are widely circulated, scientific studies
have not definitively proven that alkaline water offers these benefits.
5. Health Benefits of Regular Water
Regular water may not have the
"buzz" around it like alkaline water, but it’s no less important for
your health. Here are some of the critical health benefits of drinking regular
water:
●
Essential Hydration: (H3) Regular water is
crucial for maintaining hydration, which supports bodily functions like
temperature regulation, digestion, and the transport of nutrients and waste.
Staying hydrated is essential for energy, cognitive function, and overall
wellness.
●
Supports Digestion and Detoxification: (H3)
Regular water aids digestion by breaking down food and helping nutrients to be
absorbed. It also supports the kidneys and liver in flushing out toxins,
preventing dehydration, and reducing the risk of urinary tract infections or
kidney stones.
●
Electrolyte Balance: (H3) Regular water,
especially if it's mineral-rich, helps maintain electrolyte balance, which is
critical for muscle function and nerve transmission. This is why athletes often
need more than just plain water—they may require water with added electrolytes
after intense exercise.
●
Preventing Dehydration: (H3) Dehydration can
lead to fatigue, dizziness, and more serious health complications. Regular
water is your most straightforward and effective tool for avoiding dehydration.
6. Does Alkaline Water Have Any Risks?
While alkaline water is generally
considered safe for most people, there are a few risks to be aware of:
●
Overconsumption: (H3) Drinking too much
alkaline water can potentially lead to a condition called alkalosis, which occurs when your body’s pH becomes too alkaline.
Symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, muscle twitching, and confusion.
●
Side Effects: (H3) Excessive alkaline water
intake may also cause gastrointestinal issues, such as bloating or indigestion,
especially in people who are sensitive to changes in pH.
●
Who Should Be Cautious: (H3) People with kidney disease or those taking certain
medications should consult a healthcare provider before switching to alkaline
water. The kidneys play a key role in regulating the body's acid-base balance,
and drinking alkaline water could interfere with this delicate process.
7. Cost Comparison: Is Alkaline Water Worth the Price?
Alkaline water is often marketed at a
premium price compared to regular water. Bottled alkaline water typically costs
more per gallon, and home filtration systems (like water
ionizers) can also be quite expensive.
However, many experts argue that regular
water offers the same basic hydration benefits at a fraction of the cost.
Unless you have a specific medical condition that benefits from alkaline water,
or you prefer the taste, the extra cost might not be justified by the health
benefits.
8. How to Choose the Right Water for You
Ultimately, the best water for you
depends on your individual needs and lifestyle. Here are some factors to
consider:
●
Taste: (H3) If you prefer the taste of
alkaline water, go for it. Some people report that it tastes smoother or
cleaner than regular water.
●
Health Needs: (H3) If you suffer from acid
reflux, or you’re an athlete looking for extra hydration, you might benefit
from alkaline water. For general hydration, however, regular water is
sufficient.
●
Budget:
(H3) Regular water is much more affordable than alkaline water, so if cost
is a concern, regular water is a reliable choice.
●
Environmental Impact: (H3) Don’t forget to
think about sustainability. While both bottled regular and alkaline waters come
in plastic bottles, investing in a high-quality water filter for your home can
reduce your environmental footprint.
Both alkaline and regular water offer
essential hydration and various health benefits, but they serve different
purposes. Alkaline water is marketed for its potential to improve hydration,
balance the body's pH, and provide antioxidant properties, though many of these
claims are still not conclusively backed by science. Regular water, on the
other hand, remains a reliable, affordable, and essential part of a healthy
lifestyle. Ultimately, the best choice comes down to your personal preferences,
health goals, and budget. Whether you stick with regular water or opt for the
extra minerals in alkaline water, the key is staying hydrated and maintaining a
healthy lifestyle.
Ready to make an informed decision about
your hydration? Whether you’re curious about the potential benefits of alkaline
water or simply want to know more about the water you’re drinking every day,
Chanson Water has you covered. Explore our advanced filtration systems and
alkaline water solutions to experience the difference for yourself.
Stay hydrated, and stay healthy —
discover your ideal water today! https://chansonqualitywater.com/water-ionizer
Under sink water purifiers offer a convenient way to access clean drinking water. This guide covers their benefits, types, and installation tips to help you choose the best system.
In today’s world, access to clean and safe drinking water is more critical than
ever. Water purification plays a vital role in ensuring that the water we
consume is free from harmful contaminants. Among various purification systems
available, under sink water purifiers have gained significant popularity due to
their efficiency and convenience. This blog aims to provide a comprehensive
guide on under sink water purifiers, including their features, benefits,
installation process, and maintenance tips.
What is an Under Sink Water
Purifier?
An under sink water purifier is a
filtration system installed beneath your kitchen sink to provide clean drinking
water directly from your tap. Unlike countertop purifiers or whole-house
systems, under sink models are designed to be out of sight, maximizing counter
space while delivering high-quality water.
Comparison with Other
Water Purification Systems
●
Countertop Purifiers: These are easy to
install and portable but can take up valuable counter space and may not filter
as thoroughly.
●
Whole-House Systems: These purifiers provide
clean water throughout your home but often come with higher installation costs
and require more maintenance.
Benefits of an Under Sink
Water Purifier
- Space-Saving Design: Under sink purifiers fit neatly out of sight, freeing up counter
space for other uses.
- Improved Water Quality:
They effectively remove contaminants such as chlorine, lead, and bacteria,
ensuring cleaner, safer drinking water.
- Convenience: Enjoy purified
water directly from the tap, making hydration easier and more appealing.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Over time, under sink purifiers can save money compared to
purchasing bottled water.
Types of Under Sink Water
Purifiers
- Reverse Osmosis (RO)
Systems:
○
Functionality: Use a semipermeable membrane to
remove impurities.
○
Pros: Highly effective at removing a wide
range of contaminants.
○
Cons: Can waste water and may require more
maintenance.
- Activated Carbon Filters:
○
Functionality: Use carbon to absorb
impurities.
○
Pros: Effective for removing chlorine and
improving taste.
○
Cons: Less effective against heavy metals and
bacteria.
- Ultraviolet (UV) Purifiers:
○
Functionality: Use UV light to kill bacteria
and viruses.
○
Pros: Chemical-free disinfection.
○
Cons: Doesn’t remove chemical contaminants or
sediment.
- Multi-Stage Filtration Systems:
○
Functionality: Combine various filtration
methods for comprehensive purification.
○
Benefits: Provide balanced filtration,
targeting a wide range of contaminants.
How to Choose the Right Under
Sink Water Purifier
- Assess Your Water
Quality: Conduct a water test to identify
specific contaminants present in your water supply.
- Determine Capacity and Flow Rate: Choose a system that meets your household's needs based on daily
water consumption.
- Consider Filter Lifespan and Replacement Costs: Understand how often filters need to be changed and their
associated costs.
- Look for Certifications: Ensure the purifier meets industry standards, such as NSF/ANSI
certifications, for safety and effectiveness.
Installation Process
Overview of DIY vs.
Professional Installation
While some may choose to hire a
professional, many under sink water purifiers are designed for DIY
installation, making them accessible for homeowners.
Step-by-Step Guide for
DIY Installation
- Gather Tools: Common tools include a wrench, screwdriver, and Teflon tape.
- Shut Off Water Supply:
Always turn off the water supply before beginning installation.
- Install the Faucet: Mount
the new faucet (if applicable) according to the manufacturer’s
instructions.
- Connect the Tubing: Attach
the water lines from the purifier to the faucet and the water supply.
- Check for Leaks: Once everything is connected, turn the water supply back on and
check for leaks.
Addressing Common
Installation Challenges
●
Low Water Pressure: Ensure all connections are
tight and there are no kinks in the tubing.
●
Unusual Sounds: Check for air bubbles in the
system; they usually resolve themselves after a short time.
Maintenance Tips for Your
Under Sink Water Purifier
- Regular Filter
Replacement: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines
for replacing filters to maintain water quality.
- Cleaning Tips: Clean the
unit and faucet periodically to prevent buildup.
- Troubleshooting Common Issues:
○
Low Water Pressure: Check for clogs or ensure
the faucet is fully open.
○
Unusual Tastes: Replace filters and check for
any system malfunctions.
FAQs About Under Sink Water
Purifiers
●
How long do filters last? Filter lifespan
varies by system and usage, typically ranging from 6 months to 2 years.
●
Can I install it myself? Yes, many systems are
designed for DIY installation, with clear instructions provided.
Under sink water purifiers offer a
practical and efficient solution for accessing clean drinking water in your
home. By assessing your individual needs and understanding the various options
available, you can make an informed decision about investing in one. Whether
you choose to install it yourself or seek professional help, the benefits of
improved water quality and convenience are well worth it. Start your research
today, and enjoy the peace of mind that comes with having safe, purified water
at your fingertips!
Discover the top five reasons to invest in a water ionizer for your home, from health benefits and improved taste to cost savings and a positive environmental impact.
In today’s health-conscious world, the
quality of the water we consume has become a focal point for many individuals
and families. As awareness grows about the potential impacts of water quality
on health, people are increasingly turning to innovative solutions like water
ionizers. These devices not only enhance the properties of drinking water but
also promise a range of health benefits. This blog post explores the top five
reasons why investing in a water ionizer for your home is a decision that could
lead to significant improvements in your health and well-being.
Reason 1: Health Benefits of
Alkaline Water
One of the standout features of water
ionizers is their ability to produce alkaline water. This type of water has a
higher pH level than regular tap water, and many
proponents claim that it can help neutralize acidity in the body. The human
body tends to become more acidic due to various factors, including diet,
stress, and environmental toxins. An overly acidic environment can lead to a
host of health problems, including fatigue, digestive issues, and even chronic
diseases.
Drinking alkaline water is thought to
help restore the body’s natural pH balance, potentially leading to improved
hydration and better overall health. Some studies have suggested that alkaline
water can enhance hydration efficiency, which is essential for maintaining
energy levels and optimizing bodily functions. Improved hydration can also lead
to better digestion, as water plays a crucial role in helping the body absorb
nutrients and eliminate waste.
Moreover, there are various expert
opinions and anecdotal evidence supporting the health benefits of alkaline water. Many nutritionists
and wellness advocates recommend it as a means to support a healthier
lifestyle. While scientific research on alkaline water is still evolving, the
positive testimonials from users and some preliminary studies make a compelling
case for its potential advantages.
Reason 2: Improved Taste and
Quality of Water
Another compelling reason to invest in a
water ionizer is the noticeable improvement in the taste and quality of your
drinking water. Water ionizers utilize a process called electrolysis, which
separates the water into alkaline and acidic components. This process not only
alters the pH but also helps remove impurities such as chlorine, heavy metals,
and other contaminants commonly found in tap water.
Many people who switch to alkaline water
from a water ionizer
report a crisp, refreshing taste that makes drinking water much more enjoyable.
This enhanced flavor can motivate individuals to drink more water throughout
the day, which is vital for staying hydrated. For those who find it challenging
to consume the recommended daily intake of water, the appealing taste of
ionized water can make a significant difference.
Additionally, the improved quality of the
water means that you can feel confident about what you are drinking. By
eliminating harmful substances and enhancing taste, water ionizers provide
peace of mind, ensuring that you and your family are consuming clean and
healthy water.
Reason 3: Cost Savings Over
Time
While the initial investment in a water
ionizer may seem significant, the long-term savings can be substantial. Many
households find themselves spending a considerable amount on bottled water each
month. For instance, if a family of four spends approximately $50 a month on
bottled water, that totals $600 a year. Over a few years, this expense can add
up to a significant sum.
In contrast, a water ionizer typically
has a one-time cost that can be recouped over time. With the ability to produce
high-quality alkaline water at home, families can dramatically reduce their
reliance on bottled water. Not only does this shift save money, but it also
eliminates the hassle of frequent trips to the store to purchase water.
Additionally, water ionizers are designed
to be durable and long-lasting, often providing years of service. When you
factor in the savings on bottled water and the longevity of the device,
investing in a water ionizer becomes a financially sound decision that pays off
in the long run.
Reason 4: Environmental
Benefits
In an age where environmental concerns
are increasingly at the forefront of our minds, the environmental benefits of
using a water ionizer cannot be overlooked. One of the most pressing issues
associated with bottled water is the plastic waste it generates. Millions of
plastic bottles are discarded every year, contributing to pollution and
environmental degradation.
By investing in a water ionizer, you can
significantly reduce your plastic consumption. No longer will you need to buy
bottled water, which means fewer plastic bottles in landfills and oceans. This
shift not only contributes to a cleaner environment but also promotes a more
sustainable lifestyle.
Moreover, using a water ionizer aligns
with broader eco-friendly practices, encouraging individuals and families to
think critically about their consumption habits. By choosing to produce your
water at home, you set a positive example for others and help raise awareness
about the importance of reducing plastic waste. Every glass of alkaline water
you pour is a step toward a greener planet.
Reason 5: Convenience and
Accessibility
Perhaps one of the most appealing aspects
of owning a water ionizer is the convenience it offers. Having a reliable
source of alkaline water at your fingertips makes it easy to stay hydrated
throughout the day. No more lugging heavy bottles home from the store or
worrying about running out of water.
Most water ionizers are designed for ease
of use, allowing you to produce alkaline water with just the push of a button.
Many models also come with customizable pH settings, enabling you to tailor the
water to your specific needs. Whether you need higher pH water for drinking,
lower pH water for cooking, or acidic water for cleaning, a water ionizer
provides versatile options to suit various applications.
This level of convenience means you can
seamlessly integrate alkaline water into your daily routine. With easy access
to clean and healthy water, maintaining proper hydration becomes effortless.
This can be especially beneficial for families with children, as it encourages
healthier drinking habits for everyone.
Investing in a water ionizer is a
multifaceted decision that can yield numerous benefits for both your health and
the environment. From the potential health
benefits of alkaline water to the improved taste and quality, cost
savings, environmental advantages, and unmatched convenience, the reasons to
make this investment are compelling.
As we become more conscious of the
importance of water quality and its impact on our overall health, a water
ionizer can serve as a valuable addition to any home. By making the switch, you
are not only prioritizing your family's health but also contributing to a more
sustainable future. Take the plunge into better hydration and healthier
living—consider investing in a water ionizer for your home today!
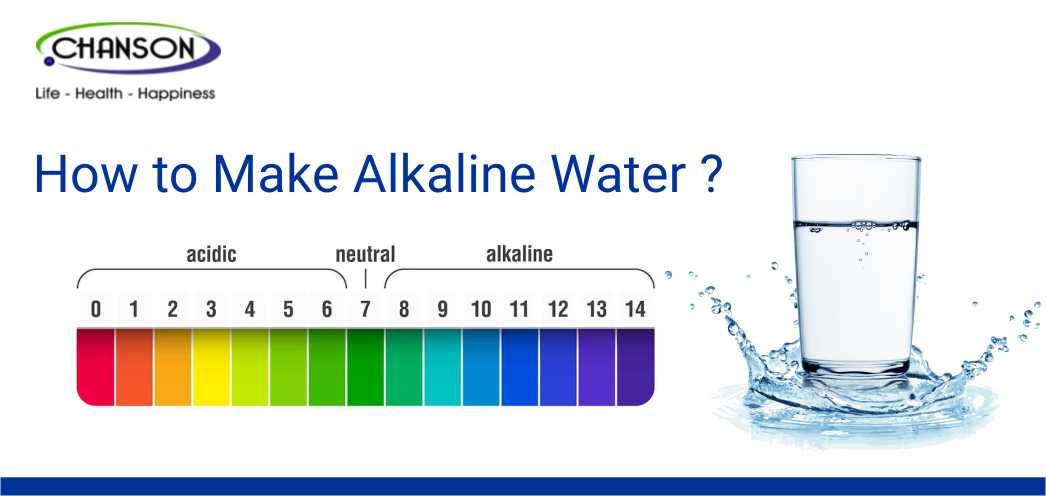
Learn how to make alkaline water at home with easy methods like baking soda and lemon. Discover its health benefits, including improved hydration and digestion!
In recent years, the health benefits of
alkaline water have gained significant attention. Many people are curious about
how to make alkaline water at home and the potential advantages it offers. In
this blog post, we will explore the different methods of making alkaline water,
the benefits associated with it, and some tips for incorporating it into your
daily routine.
What is Alkaline Water?
Alkaline water is water that has a higher
pH level than regular drinking water. While
regular water has a neutral pH of 7, alkaline water typically has a pH level of
8 or 9. The increased alkalinity is believed to neutralize acidity in the body,
which some proponents claim can lead to various health benefits. It’s essential
to understand that the pH level is just one aspect of water quality, but
alkaline water enthusiasts advocate its potential positive effects on health.
Benefits of Alkaline
Water
- Hydration: Alkaline water is often touted for its ability to hydrate more
effectively than regular water. The theory is that the smaller molecular
structure of alkaline water allows for better absorption at the cellular
level.
- Acid Neutralization:
Drinking alkaline water may help neutralize excess acidity in the body,
which can be beneficial for those consuming highly acidic diets, often
rich in processed foods and sugars.
- Antioxidant Properties:
Some studies suggest that alkaline water may have antioxidant properties,
helping to combat oxidative stress and reducing the risk of chronic
diseases.
- Improved Digestion:
Alkaline water may aid in digestion and alleviate symptoms of acid reflux.
The higher pH can help neutralize stomach acid, providing relief for those
who experience heartburn.
- Bone Health: Some research suggests that alkaline water may contribute to
bone health by reducing calcium loss in urine, which can be beneficial for
those concerned about osteoporosis.
How to Make Alkaline Water
There are several effective methods to
create alkaline water at home. Below, we outline some popular methods for
making alkaline water, along with step-by-step instructions for each.
1. Baking Soda Method
Using baking soda is one of the simplest
ways to make alkaline water.
Ingredients:
●
1/8 teaspoon of baking soda
●
1 liter of water
Instructions:
- Measure the Baking Soda: Use a measuring spoon to accurately measure 1/8 teaspoon of
baking soda. This small amount is sufficient to increase the alkalinity of
the water without overpowering its taste.
- Mix Thoroughly: Pour 1
liter of water into a clean glass or pitcher. Add the baking soda and stir
vigorously until it is completely dissolved. This ensures that the baking
soda evenly distributes throughout the water.
- Let it Sit: Allow the solution to sit for a few hours before drinking. This
resting period allows the pH to stabilize.
This method typically raises the pH of
the water to around 8 or 9, making it suitable for consumption.
2. Lemon Water Method
Although lemons are acidic, they create
alkaline byproducts once metabolized.
Ingredients:
●
1 lemon
●
1 liter of water
Instructions:
- Squeeze the Lemon: Cut the lemon in half and squeeze the juice into a measuring
cup. Aim for about 2 tablespoons of lemon juice, which is ideal for 1
liter of water.
- Mix with Water: Pour the
lemon juice into 1 liter of water and stir well to combine. The acidity of
the lemon juice will not affect the alkalinity of the water in your body
after digestion.
- Let it Infuse: For enhanced
flavor, let the mixture sit for about 30 minutes. This allows the flavors
to meld and can also slightly increase the pH.
- Serve Fresh: Drink it fresh for the best results. The lemon provides vitamin
C and adds a refreshing taste.
3. Alkaline Water
Pitchers
Another convenient option is to use
alkaline water pitchers that come with built-in filters.
Instructions:
- Fill the Pitcher: Pour tap or bottled water into the pitcher, making sure not to
exceed the maximum fill line.
- Allow to Filter: Follow the
manufacturer’s instructions for filtering. This usually takes a few
minutes as the water passes through the filter, which contains minerals
like calcium and magnesium that enhance alkalinity.
- Collect the Water: Once filtered, the water will have a higher pH level. Store it
in the refrigerator for freshness.
These pitchers are a hassle-free way to
ensure you have access to alkaline water throughout the day.
4. Ionizer Machines
For those looking for a long-term
solution, investing in an alkaline water ionizer can be worthwhile.
Instructions:
- Install the Ionizer: Follow the manufacturer’s installation instructions. This may
involve attaching it to your kitchen faucet or under the sink.
- Fill the Machine: Pour
clean water into the ionizer. Make sure to use filtered water for the best
results.
- Select pH Level: Most
ionizers allow you to choose the desired pH level, usually between 8 and
9. Some machines even offer different settings for various uses, like
cooking or cleaning.
- Collect the Alkaline
Water: Once the ionization process is complete,
collect the alkaline water in a clean container.
Ionizers not only create alkaline water
but also can enhance the overall quality of your drinking water by removing
impurities and adding beneficial minerals.
Tips for Incorporating
Alkaline Water into Your Diet
●
Start Gradually: If you’re new to alkaline
water, start with small amounts and gradually increase your intake. This will
help your body adjust.
●
Monitor Your Body: Pay attention to how your
body reacts. While many people report positive effects, it’s important to
listen to your own needs. If you experience any discomfort, consider reducing
your intake.
●
Stay Hydrated: Incorporate alkaline water as
part of your daily hydration routine but remember to drink regular water as
well. Balance is key for optimal hydration.
●
Pair with Healthy Foods: To maximize the
benefits of alkaline water, pair it with a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and
whole foods, which can also help maintain a healthy pH balance in the body.
Learning how to make alkaline water at
home is easy and can offer numerous health benefits. Whether you choose the
baking soda method, the lemon water method, or invest in an alkaline water
pitcher or ionizer, adding alkaline water to your daily routine may help
improve your overall well-being. Always consult with a healthcare professional
if you have any concerns about dietary changes. Start your journey toward
better hydration today by making alkaline water a part of your healthy
lifestyle!
By incorporating these methods and tips
into your routine, you'll be well on your way to enjoying the potential benefits of alkaline water while staying
hydrated and healthy.
Clean water is a fundamental necessity for human health and well-being. It serves as a vital resource for drinking, cooking, and sanitation, directly impacting our quality of life. The water purification process is essential in transforming untreated water into safe drinking water, helping to maintain public health and prevent the spread of diseases. Contaminated water can harbor bacteria, viruses, chemicals, and other harmful substances, making effective purification crucial in safeguarding communities.
What is the Water Purification Process?
The water purification process involves a series of steps that remove impurities from raw water, making it safe for consumption. This transformation is essential for both natural sources, such as rivers and lakes, and municipal water supplies. The process not only removes harmful contaminants but also ensures compliance with safety standards set by health authorities. Clean water is vital for hydration, food preparation, and hygiene, reinforcing the importance of understanding and implementing effective purification methods.
Key Stages of the Water Purification Process?
The water purification process consists of several key stages, each designed to tackle specific types of impurities:
a. Screening
Screening is the initial step where large debris—such as leaves, branches, and trash—is physically removed from the water. This process typically involves the use of screens or grids that catch larger particles, preventing them from entering subsequent purification stages. Effective screening is essential for protecting equipment and ensuring that the water can move smoothly through the treatment plant.
b. Coagulation and Flocculation
In this stage, chemicals known as coagulants (often aluminum sulfate) are added to the water. These chemicals cause tiny particles and impurities to clump together, forming larger aggregates called floc. The process begins with rapid mixing to distribute the coagulants evenly. Following this, the water undergoes slow mixing to allow the floc to form and grow. This step is critical because it simplifies the removal of suspended solids in the next stage.
c. Sedimentation
After floc formation, the water is transferred to sedimentation tanks, where it is allowed to sit undisturbed for a period. During this time, gravity causes the heavy floc and other suspended particles to settle at the bottom of the tank, forming a sludge layer. The clearer water, now free from many of its impurities, remains above and is ready for the next stage of purification. Sedimentation is a crucial step as it significantly reduces the turbidity of the water.
d. Filtration
The next step is filtration, where the clarified water passes through various layers of materials such as sand, gravel, and activated charcoal. This multi-layered filter system is designed to capture smaller particles, including those that remain after sedimentation. Activated carbon is particularly effective at absorbing chemicals and removing odors and tastes from the water. This step ensures that the water is not only free from visible contaminants but also safe from many dissolved impurities.
e. Disinfection
Disinfection is a vital process that ensures any remaining pathogens are eliminated. Common methods include:
● Chlorination: Adding chlorine to kill bacteria and viruses, is a widely used and cost-effective method.
● Ultraviolet (UV) Light: Exposing water to UV light, which disrupts the DNA of microorganisms, rendering them harmless without adding chemicals.
● Ozone Treatment: Using ozone gas, which is a powerful oxidant that kills pathogens and can also break down organic materials.
Disinfection is essential for producing safe drinking water, particularly in areas where microbial contamination is a concern.
f. Storage and Distribution
The final stage involves storing the purified water in reservoirs or storage tanks before it is distributed to consumers. This stage is important for maintaining the quality of the water, as it can be subjected to further contamination if not handled properly. Water distribution systems are designed to deliver clean water efficiently to homes, businesses, and public facilities, ensuring that communities have access to safe drinking water.
Types of Water Purification Processes and Systems
Several water purification systems are available, each suited for different applications:
● Reverse Osmosis (RO): This process forces water through a semi-permeable membrane that removes a wide range of contaminants, including dissolved salts, heavy metals, and microorganisms. RO systems are popular for home use due to their effectiveness.
● Ultraviolet (UV): UV purification systems use UV light to disinfect water, effectively killing bacteria and viruses without adding chemicals. These systems are ideal for treating water from wells and other sources where microbial contamination is a concern.
● Activated Carbon Filtration: This method uses activated carbon to absorb impurities, odors, and chlorine. It is effective for improving taste and removing organic chemicals.
● Ion Exchange: This process is often used to soften water by replacing hard minerals like calcium and magnesium with sodium ions. It can also remove heavy metals and other contaminants.
Why Water Quality Testing is Essential
Regular water quality testing is critical to ensure the effectiveness of the purification process. Testing can identify potential contaminants and confirm that purification systems are working correctly. Tools like Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) meters can measure the concentration of dissolved substances in the water, providing a quick assessment of water quality. Regular testing helps to detect issues before they become significant health risks, ensuring that water remains safe for consumption.
Common Contaminants Addressed by the Water Purification Process
The water purification process effectively removes a variety of contaminants, including:
● Bacteria and Viruses: Pathogens such as E. coli, Giardia, and Legionella can cause serious illnesses.
● Chemicals: Pesticides, herbicides, and industrial pollutants can leach into water supplies, necessitating their removal.
● Heavy Metals: Contaminants like lead, arsenic, and mercury pose significant health risks and are effectively removed during purification.
● Sediments and Particulates: These include silt, sand, and organic material that can affect water clarity and quality.
Understanding the water purification process is vital for ensuring access to clean drinking water. By recognizing the importance of each step—from screening to disinfection—individuals can better appreciate the efforts taken to safeguard public health. Regularly purifying and testing water not only ensures its safety but also enhances its quality. We encourage readers to explore various purification systems tailored to their specific needs or consult professionals for effective clean water solutions. Clean water is essential for health and well-being—take action today to ensure that you and your community have access to it!
Ready to enjoy pure, clean water at home? Discover Chanson Water’s innovative filtration systems today! Experience the difference and take the first step towards healthier hydration. Shop now!
https://chansonqualitywater.com/
Explore the world of Under Sink Water Ionizers with our comprehensive guide. Learn how these devices improve water quality, their key features, and the benefits they offer. Discover tips on installation, maintenance, and how they stack up against countertop models to find the best fit for your home.
1. What is an Under Sink Water Ionizer?
2. How Does an Under Sink Water Ionizer Work?
3. Benefits of Using an Under Sink Water Ionizer
4. Key Features to Consider When Choosing an Under-Sink Water Ionizer
5. Comparison: Under Sink Water Ionizer vs. Countertop Water Ionizer
6. Installation and Maintenance of an Under Sink Water Ionizer
7. Cost and Value of Under Sink Water Ionizers
8. Customer Reviews and Ratings
Access to clean and safe drinking water is crucial for health and well-being. One of the key factors in determining water quality is its TDS, or Total Dissolved Solids, content. Understanding the drinking water TDS range is essential for ensuring that the water you consume is safe and beneficial. This post delves into the importance of TDS, the safe limits for drinking water, how to measure it, and practical ways to address high TDS levels.
1. Drinking Water TDS Range: What Is Considered Safe?
TDS refers to the amount of dissolved minerals, salts, metals, and other organic substances in water. These components are naturally present in water but can vary significantly based on the source. The "drinking water TDS range" typically falls into different categories based on the concentration of these dissolved substances:
● Low TDS (0-300 mg/L): Water with low TDS is often considered pure but may lack essential minerals.
● Moderate TDS (300-600 mg/L): Generally regarded as ideal for drinking, this range balances mineral content and purity.
● High TDS (600-1,000 mg/L): While not unsafe, water in this range may have a strong taste and could cause long-term health issues.
High TDS levels can affect the taste and appearance of water and may carry contaminants, while too low a TDS might lead to water that is too soft and lacks essential minerals. Ideally, water for drinking should fall between 300-500 mg/L for both safety and taste preferences.
2. Drinking Water TDS Limit: Understanding the Standards
Various organizations have established standards to regulate the acceptable TDS limit in drinking water:
● WHO Guidelines: The World Health Organization suggests that TDS levels should be below 600 mg/L for palatability, with 300-500 mg/L being optimal.
● EPA Standards: The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has set the maximum allowable TDS level for drinking water at 500 mg/L, but this is non-enforceable and primarily based on taste considerations.
Other regional standards may vary slightly, but the common consensus is that TDS levels under 500 mg/L ensure safety and quality. These limits protect consumers from potential health risks associated with high concentrations of harmful substances like heavy metals.
3. Effects of Low TDS Levels in Drinking Water
Water with low TDS levels, typically between 0-300 mg/L, is often considered pure but may lack essential minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium that are beneficial for health. While consuming water with very low TDS is not harmful, it can lead to some drawbacks. First, the absence of these minerals can result in "soft" water, which might taste flat or bland. Over time, relying on low TDS water without sufficient mineral intake from other sources could potentially lead to mineral deficiencies, especially in areas where dietary intake of these elements is limited.
Additionally, low TDS water can be more aggressive, meaning it may absorb more contaminants from pipes and storage systems, posing a risk of contamination. For optimal taste and health benefits, a moderate TDS range (300-500 mg/L) is generally recommended.
4. Effects of High TDS Levels in Drinking Water
High TDS levels in drinking water, ranging from 600-1,000 mg/L or above, can have noticeable effects on both water quality and health. High TDS water often carries an unpleasant taste, which may be salty, bitter, or metallic, depending on the specific dissolved solids. This can make the water less palatable for everyday consumption.
From a health perspective, consuming water with high TDS over time may pose risks. Elevated levels of certain dissolved solids, such as nitrates, arsenic, or lead, can have serious health consequences, including kidney damage, hypertension, and other long-term health issues. Additionally, high TDS water may cause scaling in pipes and household appliances, reducing their efficiency and lifespan.
To maintain good water quality and avoid health risks, it's advisable to reduce TDS levels using appropriate filtration methods like reverse osmosis when they exceed the recommended limits for safe drinking water.
5. How to Use a Water TDS Meter for Accurate Measurement
A water TDS meter is a handy tool for measuring the dissolved solids in water. There are two main types: digital and analog. Digital meters are more accurate and easier to read. Here's how to use one:
● Calibration: Before testing, make sure the TDS meter is calibrated according to the manufacturer's instructions.
● Testing: Dip the meter's probe into a water sample. Ensure the probe is fully submerged for accurate reading.
● Interpreting Results: The meter will display the TDS level in parts per million (ppm). Compare the results to the recommended ranges for drinking water to assess its quality.
Maintaining the TDS meter by keeping it clean and recalibrating it regularly ensures accurate measurements over time.
6. The Impact of TDS on Drinking Water Quality
The concentration of dissolved solids significantly impacts the quality of drinking water. Water with a high TDS content often has a salty, metallic, or bitter taste and may appear cloudy. On the other hand, very low TDS levels can result in water that tastes flat or lifeless.
From a health perspective, excessively high TDS levels could contribute to kidney issues and hypertension over long-term consumption. In contrast, water with extremely low TDS may not provide enough essential minerals like calcium and magnesium. For instance, water with a TDS range of 300-500 mg/L is generally the most pleasant for drinking and offers a good balance of purity and minerals.
7. Addressing High TDS Levels: Solutions and Best Practices (H2)
If the drinking water TDS limit exceeds the recommended range, several methods can help lower the levels:
● Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems: RO filters are one of the most effective ways to reduce TDS by forcing water through a semi-permeable membrane, and removing impurities.
● Distillation: This method involves boiling water and collecting the condensed steam, leaving behind dissolved solids.
● Water Softeners: Particularly useful for high mineral content, these devices can help reduce TDS in water by replacing calcium and magnesium ions with sodium.
To maintain low TDS levels, regularly testing your water with a TDS meter and using appropriate filtration systems are key practices.
Explore the fundamentals of Oxidation Reduction Potential (ORP) in our comprehensive guide. Learn key concepts, applications, and practical insights for better understanding.
Oxidation Reduction Potential, often abbreviated as ORP, is a concept that might sound complex, but it plays a crucial role in various fields, from environmental science to industrial processes and even our own bodies. In this guide, we'll break down What is Oxidation Reduction Potential? how it works, and why it's important.
Introduction to Oxidation Reduction Potential
What is Oxidation Reduction Potential?
ORP is a measure of the ability of a substance to either gain or lose electrons during a chemical reaction. It's a key indicator of a solution's overall capacity to engage in oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions, which are processes where electrons are transferred between molecules.
Historical Background and Importance
The concept of ORP has been around for over a century. It gained prominence as scientists began to understand redox reactions, which are fundamental to many chemical and biological processes. ORP is important because it helps us predict how substances will behave in different environments, whether in a laboratory, an industrial setting, or a natural ecosystem.
The Science Behind Oxidation-Reduction Potential
How Oxidation Reduction Potential Works
At its core, ORP measures how easily a substance can either donate electrons (oxidation) or accept electrons (reduction). This is crucial in redox reactions, where one substance loses electrons, and another gains them. The higher the ORP, the more likely a substance is to gain electrons and become reduced. Conversely, a lower ORP indicates a higher tendency to lose electrons and become oxidized.
Redox Reactions Explained
Redox reactions are everywhere. For example, when iron rusts, it undergoes oxidation because it loses electrons to oxygen in the air. On the other hand, when you use bleach to whiten clothes, the bleach is being reduced as it gains electrons from the stains.
Role of Electrons in Oxidation-Reduction Potential
Electrons are the tiny particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom. In redox reactions, electrons are the main players, moving from one molecule to another. This movement of electrons is what ORP measures, giving us insight into the chemical activity of a substance.
Measuring Oxidation-Reduction Potential
Common Methods and Techniques
ORP is usually measured using an ORP meter, which consists of a probe that is dipped into the solution. The probe contains an electrode that senses the electron activity and provides a reading, usually in millivolts (mV).
Types of Electrodes Used
There are different types of electrodes used in ORP measurement, including platinum and gold electrodes. Each type has its own advantages depending on the specific application and the substance being measured.
Applications of Oxidation Reduction Potential
In Environmental Science
ORP is widely used in environmental science to monitor water quality. For example, a high ORP in water suggests that it has a strong ability to break down contaminants, making it safer to drink.
Monitoring Water Quality
Environmental scientists use ORP to assess the health of rivers, lakes, and other water bodies. A healthy body of water typically has a balanced ORP, indicating it can naturally purify itself.
Impact on Soil Chemistry
ORP also affects soil chemistry, influencing nutrient availability and microbial activity. Farmers often monitor soil ORP to ensure optimal growing conditions for crops.
In Industrial Processes
ORP plays a significant role in various industrial processes, from preventing metal corrosion to manufacturing chemicals.
Metal Corrosion and Protection
One of the most common industrial applications of ORP is in corrosion prevention. By monitoring and adjusting ORP, industries can protect metal structures like pipelines and bridges from rusting.
Chemical Manufacturing and Waste Treatment
In chemical manufacturing, ORP is used to control reactions and ensure products meet quality standards. It's also essential in waste treatment, where it helps break down harmful substances before they are released into the environment.
In Biological Systems
ORP is vital in biological systems, influencing processes like cellular respiration and even being used in medical diagnostics.
Cellular Respiration and Metabolism
In our bodies, ORP is involved in cellular respiration, the process by which cells produce energy. A balanced ORP is crucial for maintaining healthy cellular function.
Diagnostic Tools in Medicine
In medicine, ORP can be used as a diagnostic tool to assess the oxidative stress in the body, which is linked to various health conditions, including chronic diseases and aging.
Factors Influencing Oxidation Reduction Potential
Chemical Factors
Several factors can influence ORP, including the concentration of reactants and products, pH levels, and temperature.
Concentration of Reactants and Products
The concentration of substances involved in a reaction directly affects ORP. Higher concentrations typically lead to more pronounced redox reactions, altering the ORP value.
pH Levels and Temperature
pH levels and temperature also play a role in ORP. For example, acidic conditions often increase ORP, while higher temperatures can either increase or decrease ORP depending on the specific reaction.
Physical Factors
Physical factors such as electrolyte composition and environmental conditions like pressure can also impact ORP.
Electrolyte Composition
The presence of certain ions in a solution, known as electrolytes, can influence ORP by either facilitating or hindering electron transfer.
Pressure and Environmental Conditions
Environmental conditions, including pressure and the presence of other chemicals, can also affect ORP. For example, high pressure can speed up certain reactions, changing the ORP.
Understanding Oxidation Reduction Potential Through Examples
Practical Examples in Everyday Life
ORP is not just a concept for scientists; it's something we encounter in daily life.
Batteries and Fuel Cells
Batteries and fuel cells are practical examples of ORP in action. In these devices, redox reactions generate electricity, which powers everything from our smartphones to electric cars.
Common Redox Reactions
Common redox reactions include the rusting of iron, the browning of fruits, and even the metabolism of food in our bodies.
Case Studies
Environmental Monitoring Case Study
In one case study, ORP was used to monitor the health of a river system. By measuring ORP levels, scientists were able to detect pollution and take steps to restore the river's natural balance.
Industrial Application Case Study
In an industrial setting, ORP monitoring helped prevent corrosion in a chemical plant. By maintaining optimal ORP levels, the plant was able to reduce maintenance costs and extend the lifespan of its equipment.
Learn about alkalinity in water with our guide! Discover its impact on water quality, health, and the environment. Get tips on testing and managing alkalinity effectively.
Alkalinity in water is a crucial concept that often goes unnoticed by the average consumer. However, understanding what alkalinity in water means and its significance can lead to better decisions regarding water quality, health, and environmental stewardship. Alkalinity refers to the capacity of water to neutralize acids, which is essential for maintaining a stable pH level. This stability is vital for aquatic life, the safety of drinking water, and even the longevity of plumbing systems. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into what alkalinity in water is, why it's important, how it's measured, and much more.
2. What is Alkalinity in Water?
Defining Alkalinity in Water
Alkalinity in water is defined as the water's ability to resist changes in pH by neutralizing acids. This buffering capacity is primarily due to the presence of bicarbonates, carbonates, and hydroxides in the water. These substances act as a chemical shield, preventing drastic pH fluctuations that could otherwise harm aquatic environments and make water unsafe for consumption.
Chemically, alkaline water typically contains a higher concentration of bicarbonates (HCO₃⁻), carbonates (CO₃²⁻), and sometimes hydroxides (OH⁻). These ions contribute to the water's total alkalinity, which is measured in milligrams per liter (mg/L) or parts per million (ppm). The higher the concentration of these ions, the greater the water's alkalinity, and consequently, its ability to neutralize acidic substances.
3. Why is Alkalinity Important in Water?
The Importance of Alkalinity in Water Quality
Alkalinity plays a crucial role in maintaining the quality of water, both in natural bodies of water and in water used for drinking. One of the primary functions of alkalinity is to act as a buffer against rapid pH changes. In natural water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, and oceans, this buffering action is essential for the survival of aquatic life. Many aquatic organisms are sensitive to changes in pH, and a stable environment is necessary for their growth and reproduction.
In drinking water, alkalinity helps to maintain a consistent pH level, which is crucial for preventing corrosion in pipes and plumbing systems. When water is too acidic, it can corrode pipes, leading to the leaching of harmful metals such as lead and copper into the water supply. Alkaline water helps to prevent this by neutralizing acids that could otherwise cause damage. Additionally, the taste and safety of drinking water are preserved when the alkalinity is within the appropriate range.
4. How is Alkalinity in Water Measured?
Methods to Measure Alkalinity in Water
Alkalinity in water is measured using various methods, with titration being one of the most common. In titration, a known concentration of acid is added to a water sample until the pH changes to a specific endpoint, usually around 4.5. The amount of acid required to reach this point indicates the water's alkalinity, which is then expressed in mg/L or ppm.
Another method to measure alkalinity is through digital meters, which provide quick and accurate readings of the water's alkalinity levels. These meters often use electrodes to detect changes in the water's pH as acid is added. The results are displayed digitally, making it easy to monitor and adjust alkalinity levels as needed.
Understanding the units of measurement is also important. Alkalinity is typically measured in mg/L or ppm, with 1 mg/L being equivalent to 1 ppm. The ideal alkalinity range for drinking water is generally between 20-200 mg/L, depending on the source and purpose of the water.
5. Factors Affecting Alkalinity in Water
What Influences Alkalinity in Water?
Several factors can influence the alkalinity of water, both natural and human-induced. Geological formations play a significant role in determining the alkalinity of natural water bodies. For instance, water that flows through limestone-rich areas tends to have higher alkalinity due to the dissolution of calcium carbonate (CaCO₃), a major component of limestone.
Pollution and human activities can also impact water alkalinity. Industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and wastewater discharge can introduce substances that alter the water's chemical composition, either increasing or decreasing its alkalinity. Water treatment processes, such as the addition of lime or other alkaline substances, are often used to adjust alkalinity levels to meet specific water quality standards.
6. Health Implications of Alkalinity in Drinking Water
Alkalinity in Water and Its Impact on Health
The alkalinity of drinking water can have both positive and negative health implications, depending on its levels. Water with moderate alkalinity is generally considered safe and may offer health benefits by neutralizing excess acidity in the body. Some studies suggest that drinking alkaline water can help balance the body's pH, reduce acid reflux, and improve hydration.
However, water with excessively high alkalinity may have a bitter taste and could cause digestive issues in some individuals. Conversely, water with low alkalinity may be more acidic, potentially leading to corrosion in pipes and the leaching of harmful metals, which could pose health risks.
It's important to maintain a balanced alkalinity level in drinking water to ensure it is both safe and beneficial for health.
7. How to Adjust Alkalinity in Water
Methods to Increase or Decrease Alkalinity in Water
Adjusting the alkalinity of water can be necessary for various applications, from drinking water to gardening and aquarium maintenance. To increase alkalinity, substances like lime (calcium carbonate) or baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) can be added to the water. These substances increase the concentration of bicarbonates and carbonates, raising the water's buffering capacity.
To decrease alkalinity, acidic substances such as muriatic acid or sulfuric acid can be used. These acids react with the bicarbonates and carbonates in the water, reducing their concentration and lowering the alkalinity.
It's important to monitor alkalinity levels regularly, especially when making adjustments, to ensure that the water remains within the desired range for its intended use.
8. Common Myths and Facts About Alkalinity in Water
Debunking Myths Around Alkalinity in Water
There are several myths surrounding alkalinity in water, and it's important to separate fact from fiction. One common misconception is that high alkalinity automatically makes water healthier. While moderate alkalinity can have health benefits, excessively high levels can lead to adverse effects, such as digestive discomfort and an unpleasant taste.
Another myth is that alkaline water can cure diseases or significantly alter the body's pH. While alkaline water can help balance acidity, it is not a miracle cure and should not be relied upon as a sole treatment for health conditions.
The truth is that alkalinity in water is just one aspect of water quality, and it should be considered in conjunction with other factors, such as pH, mineral content, and overall water purity, to ensure that water is safe and beneficial for consumption.
Understanding alkalinity in water is essential for ensuring the quality and safety of the water we use daily. By knowing what alkalinity is, why it matters, and how to manage it, you can make informed decisions that benefit your health and the environment.

All Rights Reserved. © 2019-2026, Centrepoint Lifestyle Products Pvt Ltd.